A
abiotic component
adaptive behavior
In behavioral ecology, any behavior which contributes to an individual's reproductive success and is thus subject to the forces of natural selection.
air
See atmosphere.
allee effect
A concept in population ecology that describes the positive relationship between the size of a given population and its growth.
animals
animal behaviour
See ethology.
applied ecology
A branch of ecology which uses ecological principles and insights to solve environment-related problems. It includes agroecology and conservation biology.
aquatic plant
A vascular plant adapted to living in salt water or fresh water aquatic environments.
area effect
The biogeographic hypothesis that larger islands are able to support more species than smaller ones.
atmosphere
Earth's atmosphere is composed of gases and water which are retained by Earth's gravity and help to retain heat and reflect UV radiation.
autecology
A major sub-field of ecology which studies the dynamics of populations and the ways in which they interact with the environment. Also called population ecology.
B
behavioral ecology
A branch of ecology which studies the ecological and evolutionary basis of animal behavior, mainly at the level of the individual.
biodegradable
Capable of decaying through the action of living organisms.
biodiversity
Diversity among and within plant and animal species in a given environment.
biogeochemistry
The science that studies the effects of biota on global chemistry and on the cycles of matter and energy that transport Earth's chemical components in time and space.
biogeochemical cycle
A pathway through which a chemical element or molecule moves through the atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere.
biogeographic realm
See ecozone.
biogeography
The study of the geographic distribution of species on Earth.
bio-invader
A non-native species.
biological dispersal
The movement of organisms from their birth site to their breeding site or from one breeding site to another.
biological magnification
The increase in concentration of a chemical substance in the tissues of organisms comprising successively higher levels in a food chain.
biological organization
biomass
The sum of all living organisms in a given area.
biomass pyramid
A graph that illustrates the productivity within a trophic level Also called an ecological pyramid.
biome
The total complex of biotic communities occupying and characterizing a particular area.
biosphere
The global sum of all ecosystems on Earth.
biota
The total collection of organisms of a geographic region or a time period.
biotic component
biotic potential
The maximum achievable rate of increase of a population in a given area under ideal conditions.
boreal forest
Forest areas of the northern temperate zone, mostly consisting of conifers. Also called taiga in Siberia
C
community
An assemblage of various organisms living in the same environment.
community ecology
A branch of ecology which studies the interactions between species within an ecological community. Also called synecology.
competition
Organisms from the same or from different species competing with each other for food, living conditions, reproductive success, or any limited resource; the most adapted individuals come out on top and thus survive and reproduce.
competitive exclusion principle
A biological rule which states that two species cannot coexist in the same environment if they are competing for exactly the same resource.
coniferous forest
One of the main terrestrial biomes, culminating in the taiga.
conservation biology
The study of Earth's biodiversity which aims at protecting natural habitats and the plant and animal species living in them.
consumer
An organism, usually an animal, that feeds on plants or other animals. Compare heterotroph.
cooperation
The process by which organisms work together for mutual benefit.
coral reef
courtship display
Ritual social behavior between possible mates.
cryospherevThe combined portions of Earth's surface where water is in solid form as ice, including sea ice, lake ice, river ice, snow, glaciers, ice caps, ice sheets, and frozen ground such as permafrost. There is significant overlap with the hydrosphere
D
deciduous forest
A forest containing deciduous plants and existing where temperatures are mild and rainfall is abundant
deciduous plant
A plant that sheds all or nearly all its leaves each year
decompose
To rot or decay as a result of being broken down by microorganisms
decomposers
Organisms such as bacteria and fungi that decompose dead plants and animals;
see the food chain
deforestation
The stripping away of trees. Practices or processes that result in the conversion of forested lands for non-forest uses.
desert
A land area that receives less than 10 inches (25 cm) of precipitation a year, that loses more water through evaporation than it gains from precipitation, and that has high summer temperatures
dewpoint
The temperature at which gaseous water condenses into visible water vapor, fog or clouds
diameter
the distance from one end to another through the center; as the diameter of the earth
dilute
To lessen the strength of a material by mixing it with another material, usually water
dirty fallout
Air pollutants dropped by prevailing winds
disperse
To spread to another location
distance
the measurement from one point to another
dormant
Inactive
downcycle
Involves breaking an item down into its component elements or materials. Once the constituent elements or materials are recovered, they are reused if possible but usually as a lower-value product.
drip irrigation
The practice of spraying water directly on the base of plants so that less water is needed to help them grow
drought
An extended period of unusually low rainfall
dry deposits
Air pollutants that quickly fall to the ground without combining with moisture
E
earth
the planet where we live; see planet, and planetary facts
earthday
Special day to honor earth and going green usually with celebrations and awareness. See earthday
earth week
Usually around April 22. Week of Earth Awareness and activities. See PP Environmental Earth Calendar
earth 911 same as earth sos
The urgency to start taking care of our world for future generations
ecological community
The interaction of living organisms with their environment
ecologist
A scientist who studies organisms and their environment
ecology
The study of living things in their environment
ecosystem
A distinct area that combines biotic communities and the abiotic environments with which they interact
ecotone
The area where two or more ecosystems merge
elevation
The height above sea level
emergent layer
A forest's upper layer, produced by the tallest trees
emissions
The release of a substance (usually a gas when referring to the subject of climate change) into the atmosphere.
endangered
In immediate danger of becoming extinct
enhanced greenhouse effect
The concept that the natural greenhouse effect has been effected by emissions of greenhouse gases.
environment
The natural surroundings of an organism, which include everything, living and nonliving, that affects the organism
environmental impact
The result of our negative and positive actions on the environment.
ephemeral
An organism that has a short life cycle
epiphyte
A plant that grows on another plant in a relation ship of commensalism
equator
The imaginary boundary that divides the earth in half north and south
estivate
To spend the summer in a sleeplike condition of partial or total inactivity
evaporate
To change from a liquid to a gas as a result of being heated
evergreen
A plant whose needles or leaves remain green throughout the year
extinction
The dying out of a species of any living thing; the complete disappearance of a species from the earth, forever
extreme weather events
Scientists are worried by the increasing frequency and intensity of hurricanes, flooding, drought, as well as the loss of drinking water sources, reduction in productive farm land and increasing geographical spread of infectious diseases such as malaria.
F
fauna
All the animals in a particular area
fertilize
To join male sperm with a female egg
first-order consumers
Animals that eat plants
floor layer
A forest's sixth and bottom layer, made up of lichens and mosses growing in the remains of fallen trees, branches, and leaves
flora
All the plants in a particular area
fluorocarbons
Carbon-fluorine compounds that often contain other elements such as hydrogen, chlorine, or bromine. Common fluorocarbons include chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), and perfluorocarbons (PFCs).
fluid
Matter in a gas or liquid state
food chain (see it)
A series of organisms linked together in the order in which they feed on each other
food web
All of the interlinked food chains in a community or an ecosystem
forest
A biome whose main vegetation consists of large groups of trees that usually grow close enough together that their tops touch, shading the ground
fossil fuel
Any deposit of fossil materials, such as petroleum, natural gas, or coal, that can be burned to produce energy
fossils
Traces of the remains of prehistoric animals and plants
G
garbage
Items that are discarded also waste. Garbage often refers to food disgarded and other items to trash or waste.
eothermal energy
Heat energy from within the earth
geosphere
The soils, sediments, and rock layers of the Earth's crust, both continental and beneath the ocean floors.
global
worldwide learn about your world
global warming / climate change
The terms climate change and global warming are often used to mean the same thing. Global warming emphasises the rise in average temperatures. see global warming
grassland
A biome whose main vegetation is grass or grasslike plants
go green
Living a green lifestyle and caring for earth. recycle, recuse, reduce. learn more at earth matters
greenhouse
A structure, usually made of glass or clear plastic, that provides a protected, controlled environment for raising plants indoors
greenhouse effect
The effect of certain gasses that trap heat in the atmosphere and raise the temperature of the planet. see greenhouse effect
greenhouse gases
Atmospheric gases, mostly carbon dioxide and water vapor, that trap the warmth from the sun, just as glass traps warmth in a greenhouse
guest
Organism living on or in a host; a parasite
H
habitat
The physical place, such as a desert, forest, or single tree, where a plant or animal lives and which is usually described by its physical features; also the natural home of a community.
halocarbons
Compounds containing either chlorine, bromine or fluorine and carbon.
hazardous materials
solid or liquid materials involving or exposing one to risk (as of loss or harm)
herbivores
Animals that eat only plants; see food chain
herb layer
A forest's fifth layer, found close to the ground and containing plants such as flowers, grasses, ferns, seedling trees, and shrubs
hibernate
To spend the winter in a sleeplike condition of partial or total inactivity
host
An organism on or in which a parasite lives and whose support of the parasite often leads to its own injury
hot desert
A desert with hot daytime temperatures for most of the year
hydrocarbons
Substances containing only hydrogen and carbon. Fossil fuels are made up of hydrocarbons.
hydrosphere
liquid of earth
I
ice core
A cylindrical section of ice removed from a glacier or an ice sheet in order to study climate patterns of the past.
incinerate
To burn to ashes
insolation
The amount of solar energy that reaches the earth
insulator
A material that does not easily gain or lose energy
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
The IPCC was established in 1988 by the World Meteorological Organisation and the United Nations Environmental Programme.
J
K
kelp
Underwater forests of tall, brown algae that grow in cool coastal waters
kyoto protocol
Sponsored by the United Nations, the Kyoto Protocol is an agreement between countries to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. It was established in Japan in 1997 but didn't become international law until 2004.
L
landfill
Land waste disposal site in which waste is generally spread in thin layers, compacted, and covered with a fresh layer of soil each day
leachate
A mixture of rainwater and other liquids that comes from garbage
liquid
flowing freely like water
lichen
A combination of two organisms, fungus and green algae, that live in a relationship of mutualism
live earth
Concert for the earth held in majopr cities worldwide.
M
magma
Molten, or melted, rock within the earth
mantle
the part of the earth between the crust and the core
marine life
Plants and animals of the ocean
meteorologist
A scientist who studies the weather
methane (CH4)
A hydrocarbon that is a greenhouse gas with a global warming potential most recently estimated at 23 times that of carbon dioxide (CO2).
microorganisms
Living organisms so small they can only be seen through a microscope
midnight zone
The area of the ocean beneath the twilight zone, extending from 3,000 feet (1,000 m) down to the ocean floor, where only about 1 percent of marine life can survive
migrate
To move from one place to another
mitigation
Mitigation refers to activities which try to reduce the amount of greenhouse gases emitted into the atmosphere;
molecule
The smallest part of a substance that has all the characteristics of the substance
mountain
A biome of high ground with various types of vegetation depending on the elevation
municipal solid waste (MSW)
Residential solid waste and some non-hazardous commercial, institutional, and industrial wastes. This material is generally sent to municipal landfills for disposal.
N
natural gas
Underground deposits of gases consisting of 50 to 90 percent methane (CH4) and small amounts of heavier gaseous hydrocarbon compounds such as propane (C3H8) and butane (C4H10).
natural resources
things from nature; see earth matters
nekton
Animals, such as fish and whales, that move independently of water currents between the bottom and surface of the ocean
neutral
Having a pH of 7 and thus being neither acidic nor basic
niche
The location and role or job for which a species is well suited within its community, including its habitat, what it eats, its activities, and its interaction with other living things
node
Where leaves grow from a plant stem
nonbiodegradable
Not able to be consumed and/or broken down by biological organisms. Nonbiodegradable substances include plastics, aluminum, and many chemicals used in industry and agriculture.
nonrenewable resource
Resources exist in the earth that are non renewable because we are taking them away and using them at a much faster rate than they were formed. Examples are copper, aluminum, coal, and oil.
Northern Hemisphere
The area of the earth above the equator
Northern temperate zone
The region between latitudes 23.5¡N and 66.5¡N.
nuclear energy
Energy produced from changes in atomic nuclei
nuclei
The heavy centers of atoms
nutrition:
To be nourished: the process by which living things or organisms take in and utilize food material.
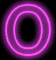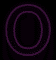
O
oceans
The largest bodies of water on earth
offsetting
Offsetting involves calculating the total amount of carbon dioxide that will be emitted from a certain activity, for example plane travel or a conference call.
omnivores
Animals that eat both plants and animals
organic
All living things, and products that are uniquely produced by living things, such as wood, leather, and sugar. 2. All chemical compounds or molecules, natural or synthetic, that contain carbon atoms as an integral part of their structure.
organism
All living things, including people, plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi
oxygen
An atmospheric gas made up of two oxygen atoms that is necessary for respiration
oxygen cycle
The recycling of oxygen-containing gases between plants and animals
ozone
A form of oxygen made up of three oxygen atoms that forms the ozone layer.
ozone cycle
The ongoing process by which ozone breaks down and re-forms in the ozone layer
ozone depletion
Damage to the ozone layer
ozone layer
Scattered molecules of ozone gas that collect in the upper atmosphere of the earth in a layer that shields the earth from excessive ultraviolet light
P
parasite
An organism that lives on or in a host organism and that gets its food from or at the expense of its host
parasitism
A relationship in which one organism, a parasite, secures its nourishment by living on or inside a host organism at the expense of its host
permafrost
A layer of permanently frozen soil underground. An important feature of a tundra
pH
The unit of measure for determining whether a solution is acidic, basic, or neutral
pH scale
The scale, ranging from 0 to 14, used to measure the pH of a solution.
photosynthesis
The process by which plants use light energy trapped by chlorophyll to change carbon dioxide and water into food
phytoplankton
Plant plankton
plankton
Small to microscopic organisms that live near the ocean's surface and are carried along by the currents. Animal plankton are called zooplankton, and plant plankton are called phytoplankton
pollutants
Substances that destroy the purity of air, water, or land
polyp
A tiny, tubelike marine animal of which live coral is made, one end of which is attached to the sea bottom, to rocks, or to one another and the opposite end of which is a mouth surrounded by fingerlike, stinging tentacles
population
Organisms of the same species living together in a specific area; also the total count of individuals in a specific area, such as the population of a town, see the world population
precipitation
Water that returns to the earth as rain, hail, sleet, or snow
precycle, precycling
Conciousness about what you buy and use and choosing products based on less waste reduction. learn about precycling
predator
An animal that hunts and kills other animals for food
prevailing winds
Winds that blow consistently from one direction
producers
Organisms (specifically, plants) that can produce their own food, see food chain
Q
R
radiation
Energy transfer in the form of electromagnetic waves or particles that release energy when absorbed by an object.
recycle
To use again; see Planetpals recycle center
recycling
Collecting and reprocessing a resource so it can be used again.see Planetpals recycle center
reduce
Using less
reforestation
Planting of forests on lands that have previously contained forests but that have been converted to some other us
renewable
Able to be replaced or replenished, either by the earth's natural processes or by human action. Air, water, and forests are often considered to be example of renewable resources.
Refuse Another name for waste
renewable energy
Known as green or environmentally-friendly energy, renewable energy comes from natural sources that won't run out. These include the wind, the sun, the waves and biofuels such as wood, manure or flaxseed oil
renewable resource
Resources exist in the earth that are non renewable because we are taking them away and using them at a much faster rate than they were formed. Examples are copper, aluminum, coal, and oil.
Rewilding Restoring the habitat for natural species
repair
To fix
respiration
An ongoing process by which plants and animals take in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide
reuse
use something another time; see earth matters
S
sanitary landfill
A solid waste disposal area that protects the environment from leachate
savannah
A land which is without trees but with much grass either tall or short (such as the African savannah)
scrub
Plants, such as small trees and shrubs, that usually have many stems, unlike trees which have one main trunk
sea level
The level of the surface of the ocean
second-order consumers
Animals that eat first-order consumers
semiarid
Having a climate that is dry, but not as dry as a desert
sink
Any process, activity or mechanism which removes a greenhouse gas, an aerosol or a precursor of a greenhouse gas or aerosol from the atmosphere
social group
A small population that lives and travels together and in some ways depends on each other for its well-being
soil erosion
The wearing away of the soil by wind or water
solar energy
Energy from the sun
solar radiation
Radiation emitted by the Sun.
solution
A mixture made by dissolving a substance in a liquid, such as water
Southern Hemisphere
The area of the earth below the equator
southern temperate zone
The region between latitudes 23.5¡S and 66.5¡S
species
A group of similar and related organisms
stern review
In 2006, economist Sir Nicholas Stern published a report - The Stern Review - on the economics of climate change.
stomata
Tiny pores on the surface of plant leaves that can open and close to take in and give out water vapor
stratus
Clouds which are produced by stable air and looks like an even blanket
stratonimbus
Stratus clouds which produce a steady rainfall
streamflow
The volume of water that moves over a designated point over a fixed period of time.
subcanopy layer
A forest's third layer, formed by the leaves and branches of shorter trees under the canopy layer
sublime climate change
The change in the climate caused by global warming. see sublime climate change
succulent plants
Plants that have thick, fleshy leaves or stems for storing water
sunlight zone
The upper 488 feet (150 m) of the ocean, where sunlight penetrates and where about 90 percent of all marine life live
superorganism
An organism, such as coral or the Portuguese man-of-war, that appears to be one organism, but in fact is a number of colonial animals joined together
sustainability
To keep in existence; maintain. To supply with necessities or nourishment; provide for earth also sustainable living.
T
third order consumers
Animals that eat first- and/or second-order consumers
threatened species
Wild species that is still abundant in its natural range but is likely to become endangered because of a decline in numbers.
top consumer
An organism at the top of a food chain
trace gas
Any one of the less common gases found in the Earth's atmosphere.
transpiration
The loss of water into the atmosphere through the stomata of plants
trash
Items that are discarded also waste.
tree line
The height on a mountain above which the climate is too cold for trees to grow
tropical rain forest
A forest that gains more water from precipitation than it loses through evaporation. Located in the tropical zone and having an average temperature between 70¡ and 85¡F (21¡ and 29¡C) and average yearly rainfall of more than 80 inches (200 cm)
tropical zone
The region between latitudes 23.5¡S and 23.5¡N
tundra
A treeless biome mainly in the north polar areas that has long frigid winters and brief summers and where grasses, mosses, lichen, low shrubs, and a few flowering plants survive
twilight zone
The shadowy area of the ocean, extending from the bottom of the sunlight zone down to about 3,000 feet ( l ,000 m), where plants cannot grow and where animals are less numerous and smaller
High-energy rays of sunlight
U
upcycle
To reuse (discarded objects or material) in such a way as to create a product of a higher quality or value than the original.
urban heat island
Buildup of heat in the atmosphere above an urban area.
universe
The solar system beyond our world; see universe
 |

Top Ten Toy: Planetpals Puzzle!
Rated among top ten for this season!
5 puzzles available
Learn more |

|
Planetpals Activity Books

|
Planetpals Products  |
Learn about habitats with King Dom |
|